Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by an infestation of the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. This parasitic mite burrows into the skin, causing intense itching and discomfort. Although treatable, scabies can spread rapidly through close personal contact, making it a significant public health concern in certain environments such as nursing homes, prisons, and crowded living conditions. Permethrin Lotion and Scabper Lotion is an antiparasitic medication. It is used to treat scabies, a condition where tiny insects infest and irritate your skin.
Symptoms of Scabies:
The primary symptom of scabies is severe itching, which typically worsens at night or after a hot shower. This itching is the result of the mites burrowing into the skin to lay eggs and their saliva triggering an allergic reaction. Common areas affected include:
- Between Fingers: Mites prefer the webbing between fingers and toes.
- Wrists, Elbows, and Armpits: These warm areas are favorable for mite infestation.
- Genitals: Particularly in men and children.
- Nipples: More common in women, especially those who are breastfeeding.
- Buttocks and Waist: Areas where clothing fits snugly.
It’s essential to note that symptoms may take several weeks to appear after initial infestation, especially if it’s the first time the person has had scabies. In individuals who have had scabies before, symptoms may appear within a few days.
Causes of Scabies:
Scabies spreads through prolonged, close skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. This could happen in various situations:
- Household Contacts: Sharing bedding, towels, or clothing with someone who has scabies.
- Sexual Contact: Scabies can be sexually transmitted, although this is less common.
- Childcare Facilities: Easily spread among children due to close contact and shared spaces.
- Healthcare Settings: Particularly in long-term care facilities where residents have prolonged contact with healthcare providers.
Once a mite infests a new host, it burrows into the skin, where it lives and reproduces. Female mites lay eggs in these burrows, which hatch and mature into adult mites over the course of a few weeks.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing scabies usually involves examining the skin and identifying characteristic signs such as burrows, nodules, and intense itching in typical areas. A healthcare provider may also use a microscope to look for mites, eggs, or fecal matter (scybala) taken from the skin. In cases where the diagnosis is unclear or complicated, a skin scraping or biopsy may be performed.
Treatment Options:
Treating scabies typically involves killing the mites and their eggs, as well as managing the associated symptoms:
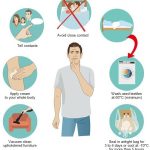
- Topical Medications: Permethrin cream is commonly prescribed, which kills both the mites and their eggs. It’s applied to the entire body from the neck down and washed off after 8-14 hours.
- Oral Medications: In severe cases or when topical treatments fail, oral ivermectin may be prescribed.
- Symptom Management: Antihistamines or topical steroids can help relieve itching and inflammation.
Additionally, all household members and close contacts should be treated simultaneously to prevent re-infestation. Bedding, clothing, and towels should be washed in hot water and dried on high heat to kill any mites or eggs that may be present.
Complications:
If left untreated, scabies can lead to secondary infections such as impetigo (a bacterial skin infection) or cellulitis (a bacterial infection of the deeper layers of the skin). These complications can cause further discomfort and require additional medical treatment.
Preventing Scabies:
Preventing scabies involves practicing good hygiene and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Steps to prevent scabies include:
- Avoiding Sharing Personal Items: Such as clothing, towels, or bedding with someone who has scabies.
- Maintaining Cleanliness: Regular handwashing and bathing can reduce the risk of transmission.
- Treating Contacts Promptly: If someone in your household or close circle is diagnosed with scabies, seek treatment for everyone who has had close contact.
Conclusion:
Scabies is a distressing condition caused by a parasitic mite that burrows into the skin, causing intense itching and discomfort. While highly contagious, scabies is treatable with topical medications like permethrin and, in some cases, oral medications like ivermectin. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and further spread of the infestation. Practicing good hygiene and avoiding close personal contact with infected individuals are crucial in preventing scabies outbreaks. If you suspect you or someone you know has scabies, seek medical advice promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In summary, while scabies can be challenging to deal with due to its contagious nature, with proper medical care and hygiene practices, it can be effectively managed and treated.